Hydrogenated Rosin
Introduction
It is a high quality, modified rosin from the WW grade (or other grades as per request) through the process of hydrogenation.
Hydrogenated rosin has a high antioxidation and thermal stability, strong adhesion, and ensures the advantages of long-term flexibility and light color.
Description
A common method to improve stability is to hydrogenate the rosin molecules as shown in the figure.
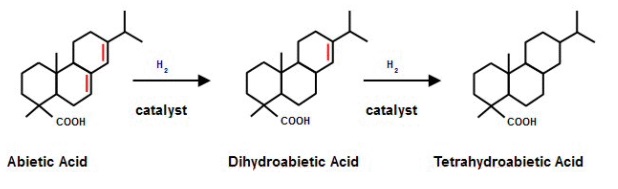
Hydrogen molecules add to the double bonds of the rosin acid which greatly increases the molecule’s resistance to oxidation and improves its color. The hydrogenation process can be controlled so that the rosin is either partially or fully hydrogenated.
Properties
Like rosin resins, hydrogenated rosin resins have a wide span of compatibility with almost all polymers. They are well known for their peel and tack contribution to the adhesive. They have specific advantages over non-hydrogenated rosin resins:
- Lighter color.
- Significantly improved stability.
- Less to no skin sensitization (depends on the degree of hydrogenation).
- Less UV absorption, thus making them suitable for UV curable polymer based adhesives.
- Imparts only a slight decrease of cohesive strength, especially in block co-polymer systems.
- Can be used in amorphous polyolefin based adhesives.
Application/Usage
It is mainly used as raw material for adhesives and inks, and in the manufacture of synthetic rubbers especially for tires. It also finds application in the electronic fields such as manufacture of solder flux, soldering wires etc.
Also used in production of edible ester gum, paper and soap.



